As decentralized finance and Web3 platforms continue to expand, the need for robust, privacy-conscious compliance tools has never been greater. One of the most effective ways to safeguard your project against fraud and regulatory risk is by building a secure allowlist using onchain attested KYC addresses. This approach not only ensures that only verified users can access your platform or participate in token sales, but also leverages the transparency and immutability of blockchain technology to maintain trust among stakeholders.

Why Onchain Attested KYC Matters for Secure Allowlists
The traditional allowlist model relies on off-chain databases or manual processes to vet participants. While functional, these systems are prone to data breaches, human error, and lack transparency for both users and auditors. By contrast, onchain attested KYC solutions issue cryptographic proofs directly to blockchain addresses after successful verification. These attestations are tamper-proof, instantly verifiable by smart contracts, and portable across compatible ecosystems.
With the current Ethereum (ETH) price at $4,463.43, according to real-time data, the stakes for secure participation in DeFi protocols and token launches are higher than ever. Allowing only verified addresses through your allowlist helps prevent sybil attacks, reduces compliance headaches, and creates a more trustworthy environment for all participants.
Core Components of a Blockchain-Based Allowlist
Essential Features for a Secure Blockchain Allowlist
-
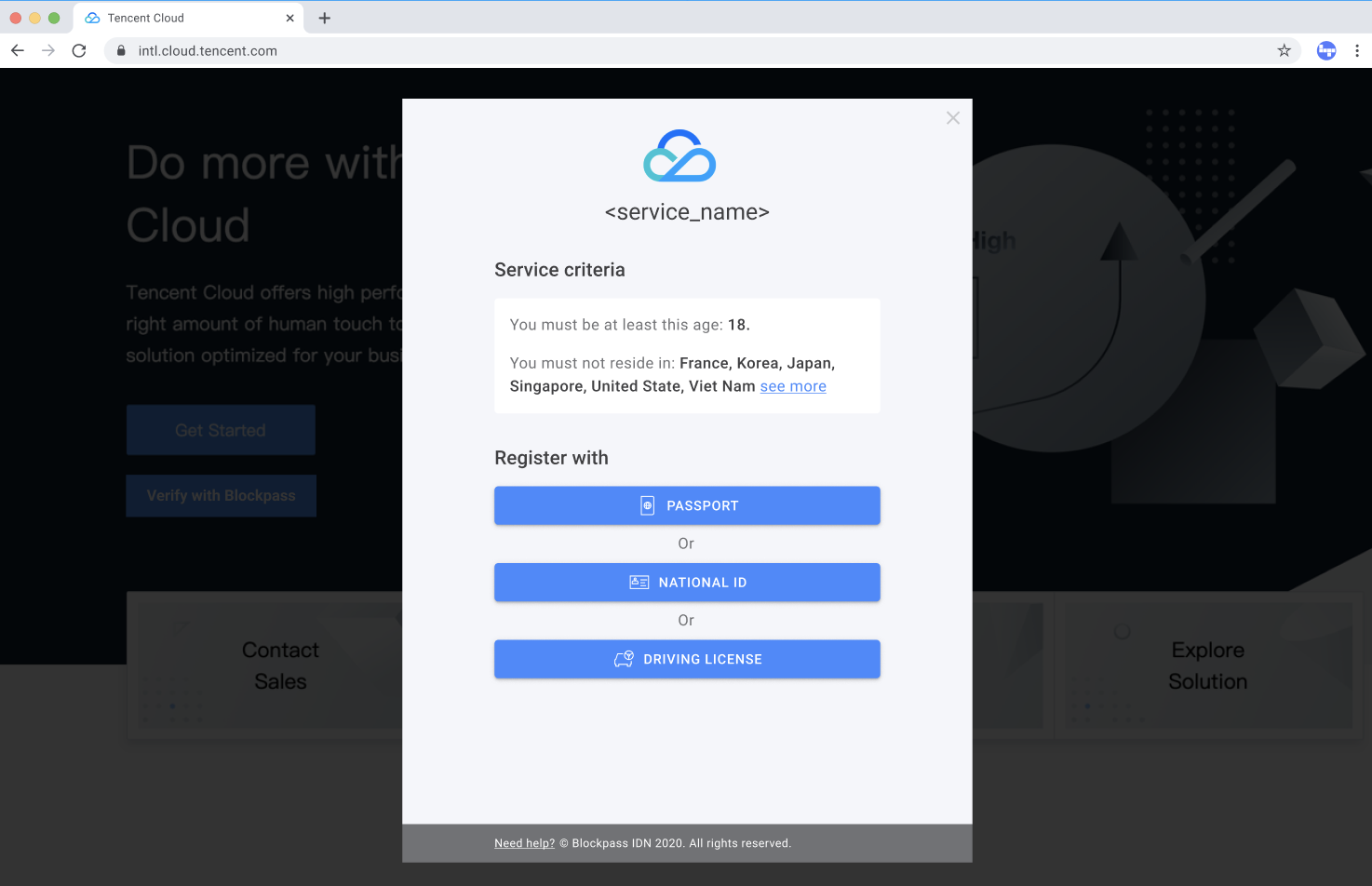
On-Chain KYC Attestations: Leverage established providers like Blockpass or PureFi Protocol to issue verifiable, tamper-proof KYC attestations directly on the blockchain, ensuring only verified users are allowlisted.
-
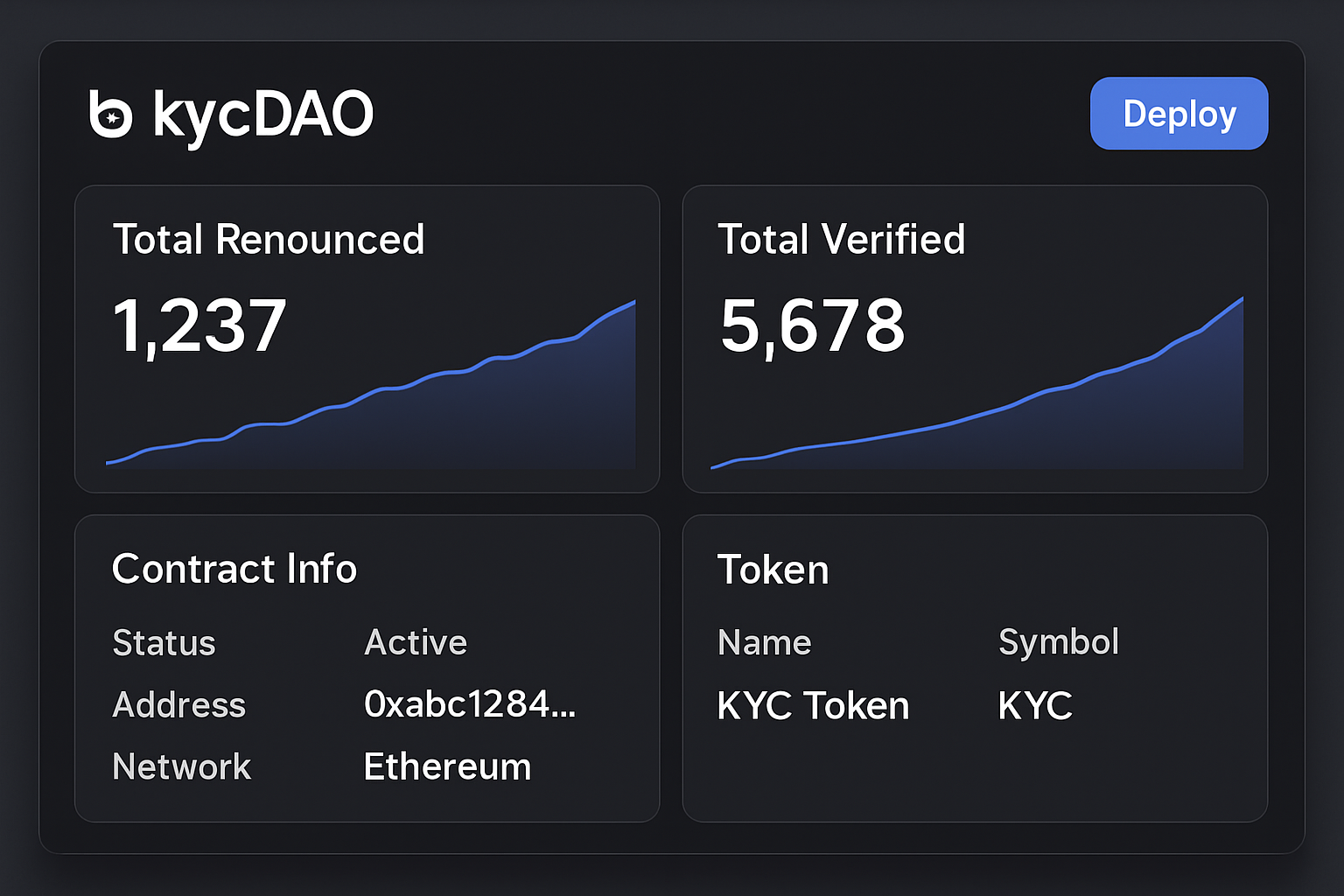
Smart Contract-Based Allowlist Management: Use programmable smart contracts—such as those from kycDAO—to automatically check wallet addresses for valid KYC attestations before granting access, minimizing manual errors and enhancing transparency.
-

Privacy-Preserving Verification: Implement zero-knowledge proof solutions (e.g., 0xKYC) to verify user compliance without exposing sensitive personal data, aligning with privacy regulations and user expectations.
-

Granular and Dynamic Access Controls: Adopt compliance engines like Chainlink ACE to enforce real-time, policy-based allowlist requirements and eligibility, adapting to changing regulations or risk profiles.
-

Continuous Monitoring and Revocation: Integrate systems that regularly monitor KYC status and allow for swift revocation of access if compliance lapses, using solutions like Palisade for real-time allowlist management.
-
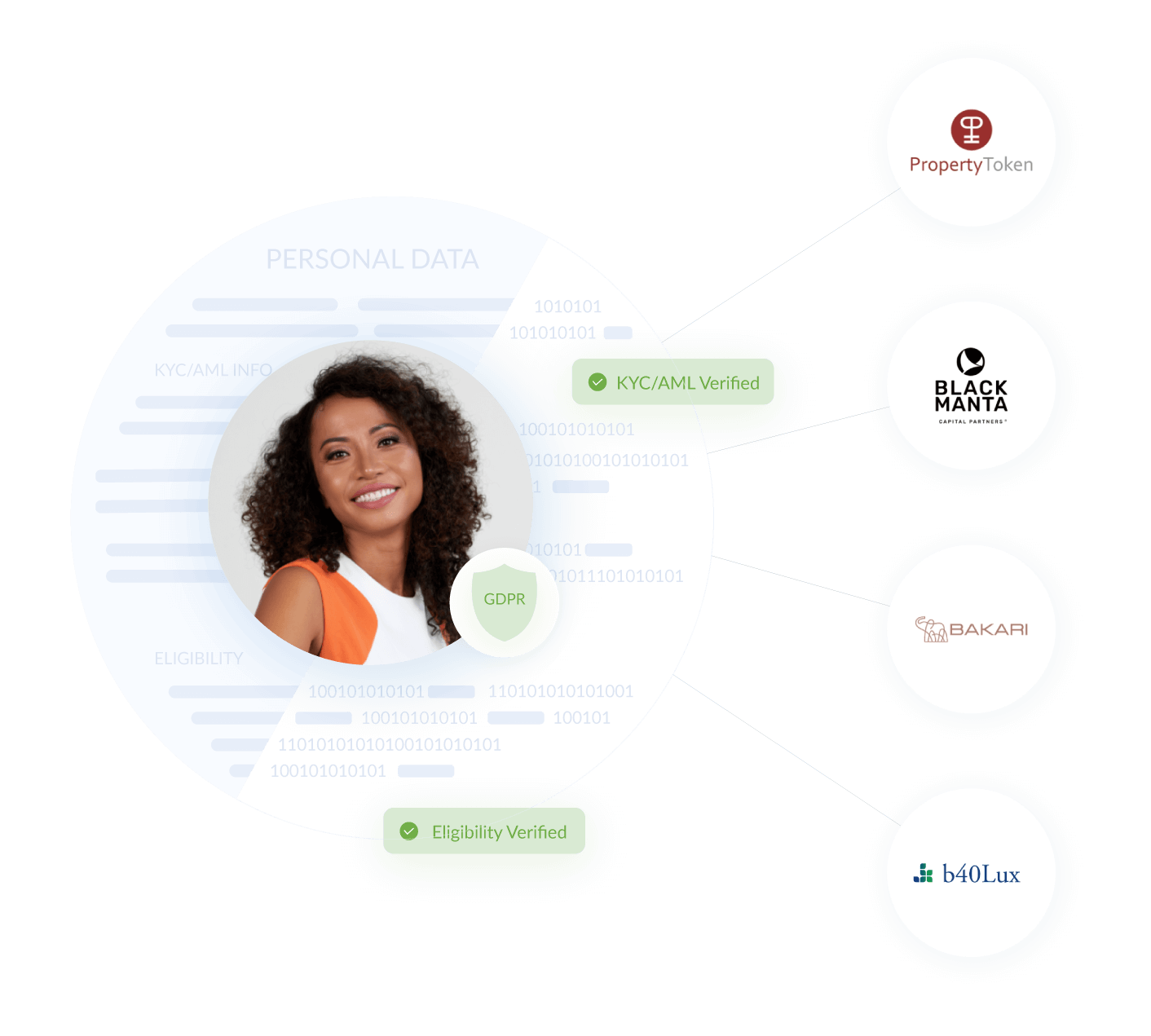
User-Friendly Identity Management: Employ decentralized identity solutions such as ONCHAINID to give users control over their digital identity, improving onboarding and trust.
The backbone of any secure allowlist powered by onchain attested addresses consists of several interlocking components:
- Onchain KYC Verification: Providers like Blockpass offer seamless integration with smart contracts through their On-chain KYC™ protocol. This ensures that only individuals who have completed regulatory-compliant KYC checks can receive an attestation tied to their wallet address.
- Smart Contract Access Controls: Modern frameworks such as kycDAO‘s smart contracts enable real-time checks of an address’s compliance status before allowing interaction with sensitive functions or assets.
- Privacy-Preserving Verification: Zero-knowledge proof solutions ensure that while a user’s identity is verified and attested onchain, their personal information remains confidential even from platform operators.
- Allowlist Management Tools: Solutions like Palisade streamline the process of updating your allowlist as new users complete KYC or existing credentials expire.
KYC Attestations: How They Work Onchain
The journey begins when a user submits their information through a compliant provider such as Blockpass. Upon successful verification, an onchain attestation (or token) is minted directly to the user’s wallet address. This digital credential acts as an immutable stamp of approval that can be referenced by smart contracts managing your platform’s access controls. For example, kycDAO issues a kycNFT that serves precisely this function, allowing contracts to check eligibility without exposing sensitive data (see kycDAO docs).
This model not only streamlines onboarding but also empowers end-users with self-sovereign identity management, they control when and where their credentials are used across supported dApps.







