Web3 continues to redefine digital identity and compliance, with onchain attestations emerging as a transformative force for KYCed address verification. As regulatory pressure intensifies and user onboarding accelerates, projects are seeking solutions that offer both robust compliance and seamless user experience. Onchain attestations deliver exactly that: cryptographic proofs, recorded directly on blockchain networks, confirming that an address has passed Know Your Customer (KYC) checks without exposing sensitive personal data.
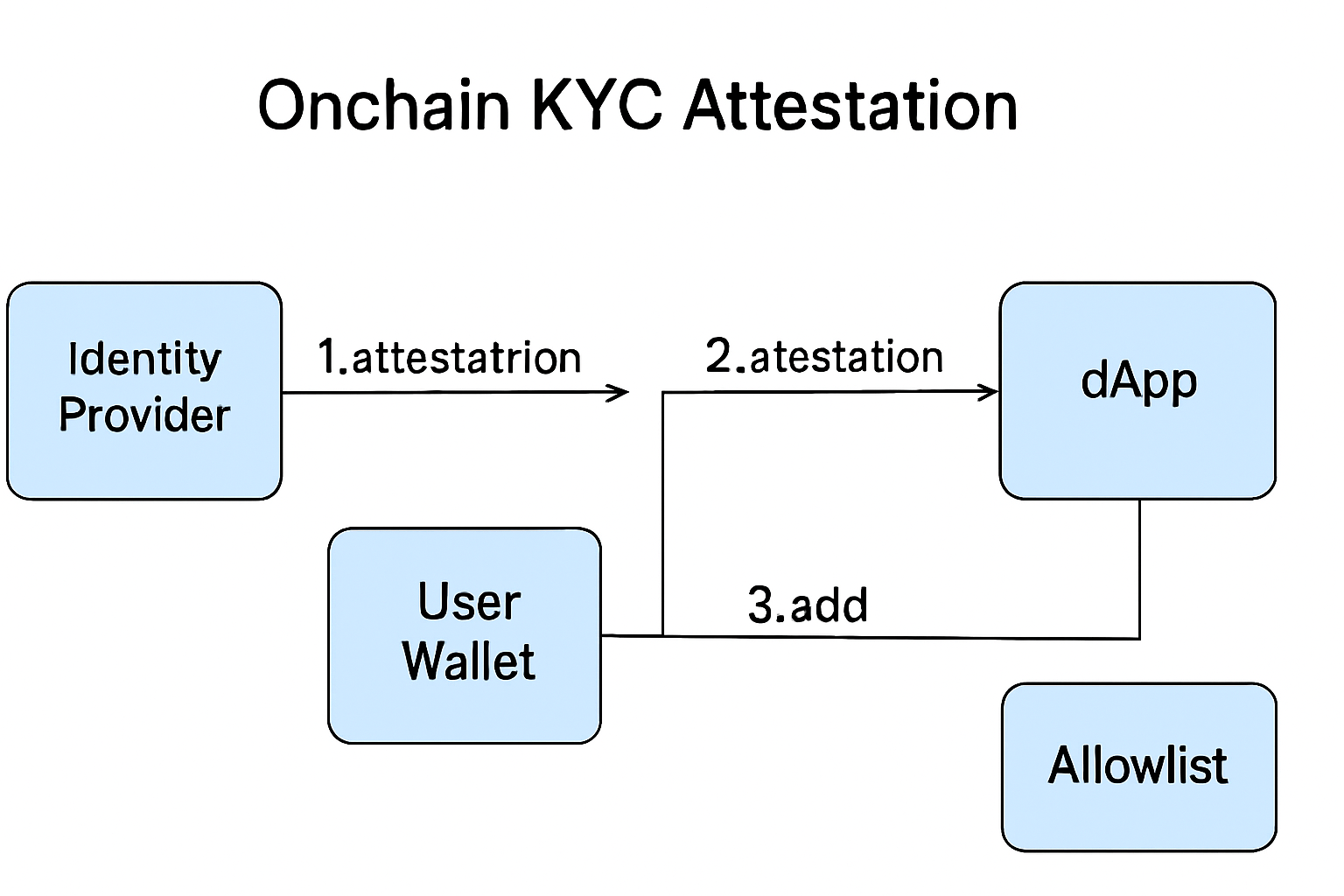
Onchain Attestations: The New Standard for Web3 Allowlist Compliance
Traditional KYC processes are slow, siloed, and often require users to repeat verification across multiple platforms. In contrast, onchain attestations enable interoperable, verifiable credentials that travel with the user across the decentralized ecosystem. This is particularly valuable for allowlists in token sales, gated DeFi communities, or NFT mints where only KYCed addresses can participate.
How does this work in practice? Once a user completes KYC with a trusted provider, an attestation is issued and anchored on-chain. Any dApp or allowlist manager can then verify the credential instantly, often with a single line of code:
Verifying KYC Status with Onchain Attestations in JavaScript
Onchain attestations enable instant, verifiable KYC checks without exposing sensitive data. Below is a JavaScript example that queries an attestation protocol to verify a user’s KYC status.
// Example: Verifying KYC status using Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS)
import { ethers } from 'ethers';
import { EAS, SchemaEncoder } from '@ethereum-attestation-service/eas-sdk';
// EAS contract address (for example, on Optimism)
const EASContractAddress = '0x4200000000000000000000000000000000000021';
const provider = new ethers.JsonRpcProvider('https://optimism-mainnet.infura.io/v3/YOUR_INFURA_KEY');
const eas = new EAS(EASContractAddress);
eas.connect(provider);
// KYC attestation UID (obtained from the user)
const attestationUID = '0x1234abcd...';
async function verifyKYCStatus(uid) {
const attestation = await eas.getAttestation(uid);
if (!attestation) {
return false; // No attestation found
}
// Example: Check if the attestation schema matches the KYC schema
const KYC_SCHEMA_UID = '0xabcde...';
if (attestation.schema !== KYC_SCHEMA_UID) {
return false;
}
// Optional: Check if attestation is revoked or expired
if (attestation.revoked || (attestation.expirationTime && Date.now() / 1000 > attestation.expirationTime)) {
return false;
}
return true; // KYC verified
}
// Usage
verifyKYCStatus(attestationUID).then(isKYC => {
if (isKYC) {
console.log('User is KYC verified');
} else {
console.log('User is NOT KYC verified');
}
});This approach streamlines compliance for Web3 allowlists, reducing manual review and leveraging cryptographic proofs for trustless verification.
This dramatically reduces both development friction and compliance risk. No more manual uploads or repeated document checks; the blockchain acts as a universal trust layer.
Privacy-Preserving Compliance: Zero-Knowledge Proofs in Action
The privacy benefits are equally significant. Instead of sharing personal information with every new project, users present cryptographic proofs, often leveraging zero-knowledge (zk) technology, that confirm their allowlist eligibility without revealing underlying identity details. This approach aligns tightly with GDPR and global privacy regulations while maintaining regulatory-grade assurance for projects.
“Onchain attestations bridge real-world identity requirements with Web3’s ethos of decentralization and privacy. “
5 Key Benefits of Onchain Attestations for KYCed Address Verification
-

1. Streamlined KYC Verification: Onchain attestations allow dApps to verify a user’s KYC status with minimal integration effort. Platforms like Attest Protocol enable developers to confirm KYC compliance with a single line of code, reducing both development time and operational complexity.
-
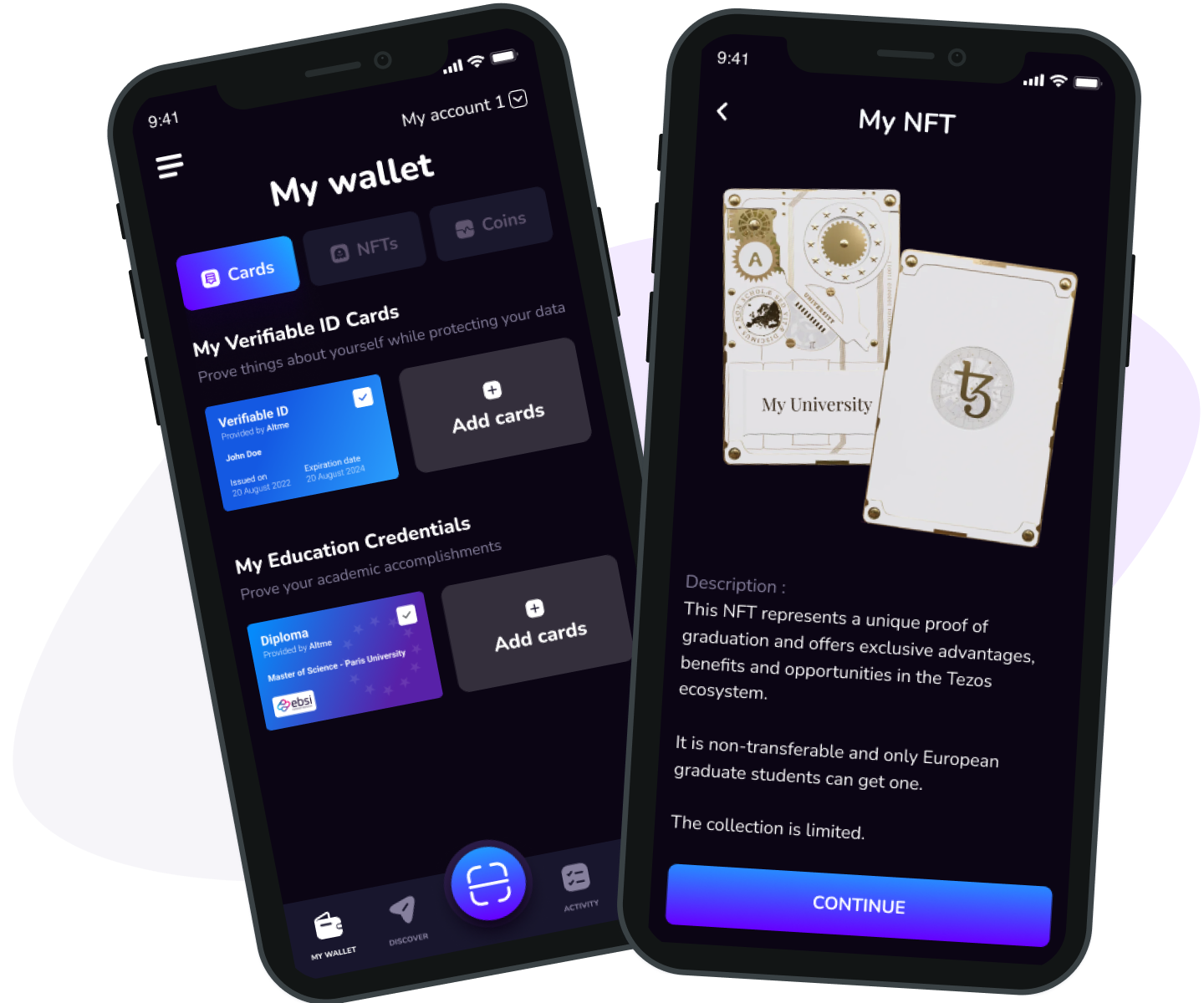
2. Enhanced Privacy for Users: Solutions such as Altme issue verifiable credentials and non-transferable NFTs, allowing users to prove KYC compliance without exposing sensitive personal data on-chain, aligning with privacy regulations like GDPR.
-
3. Cross-Platform Interoperability: Onchain attestations are blockchain-agnostic, enabling users to carry their verified credentials across multiple dApps and platforms. This eliminates repeated KYC checks and creates a more seamless user experience.
-
4. Automated Regulatory Compliance: With solutions like Chainlink Automated Compliance Engine (ACE), compliance policies can be directly enforced within smart contracts, ensuring only authorized, KYCed users can access specific assets or functions in real time.
-

5. Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: By keeping sensitive KYC data off-chain and using attestations as proof, platforms minimize the risk of centralized data leaks and breaches, strengthening overall security for both users and Web3 projects.
Real-World Adoption: Protocols Leading the Charge
The shift toward decentralized identity is not theoretical, it’s happening now across major chains:
- Altme: Issues privacy-preserving verifiable credentials and NFTs after one-time KYC via wallet integration.
- Attest Protocol: Offers schema-based attestation logic for developers to instantly check KYC status.
- Chainlink ACE: Embeds compliance policies directly into smart contracts for real-time enforcement.
This interoperability means users can move between platforms without repeating cumbersome checks, while projects maintain airtight compliance controls at scale.
The Technical Edge: Efficiency Meets Security
The advantages extend beyond convenience. Onchain attestations are immutable and tamper-resistant by design, secured by consensus mechanisms underpinning blockchains like Ethereum or Solana. For developers, this translates into reduced backend complexity and lower attack surfaces compared to legacy off-chain solutions.
If you’re building or managing an allowlist in today’s regulatory climate, adopting onchain attestations isn’t just about staying compliant, it’s about future-proofing your project against shifting standards while delivering best-in-class user experience. For more technical guidance on implementation strategies, see our deep dive at /building-a-secure-allowlist-with-onchain-attested-kyced-addresses.
Adoption of onchain attestations KYC is accelerating, with both compliance teams and developers recognizing the operational efficiency gains. By abstracting identity checks into reusable, cryptographically secure proofs, Web3 projects can automate allowlist management and drastically reduce manual review overhead. This is especially critical for high-volume token launches or DeFi protocols where rapid onboarding is a competitive necessity.
Security is not compromised in this process. Onchain attestations are anchored in blockchain consensus, making them immutable and auditable. Unlike offchain databases vulnerable to breaches or tampering, these credentials persist as long as the underlying network remains secure. For end users, this means a single KYC event can unlock participation across multiple platforms, without the risk of overexposing personal data.
Developer Experience: Integrating Attestations with Minimal Overhead
Modern attestation protocols are designed for frictionless integration. Developers can leverage SDKs and APIs that abstract away complex cryptography, focusing instead on business logic and user experience. Here’s what makes integration straightforward:
Top Developer-Friendly Features of Onchain Attestation Protocols
-
Simple API Integration: Leading protocols like Attest Protocol enable developers to verify KYC status with minimal code—often a single function call—streamlining integration and reducing complexity.
-
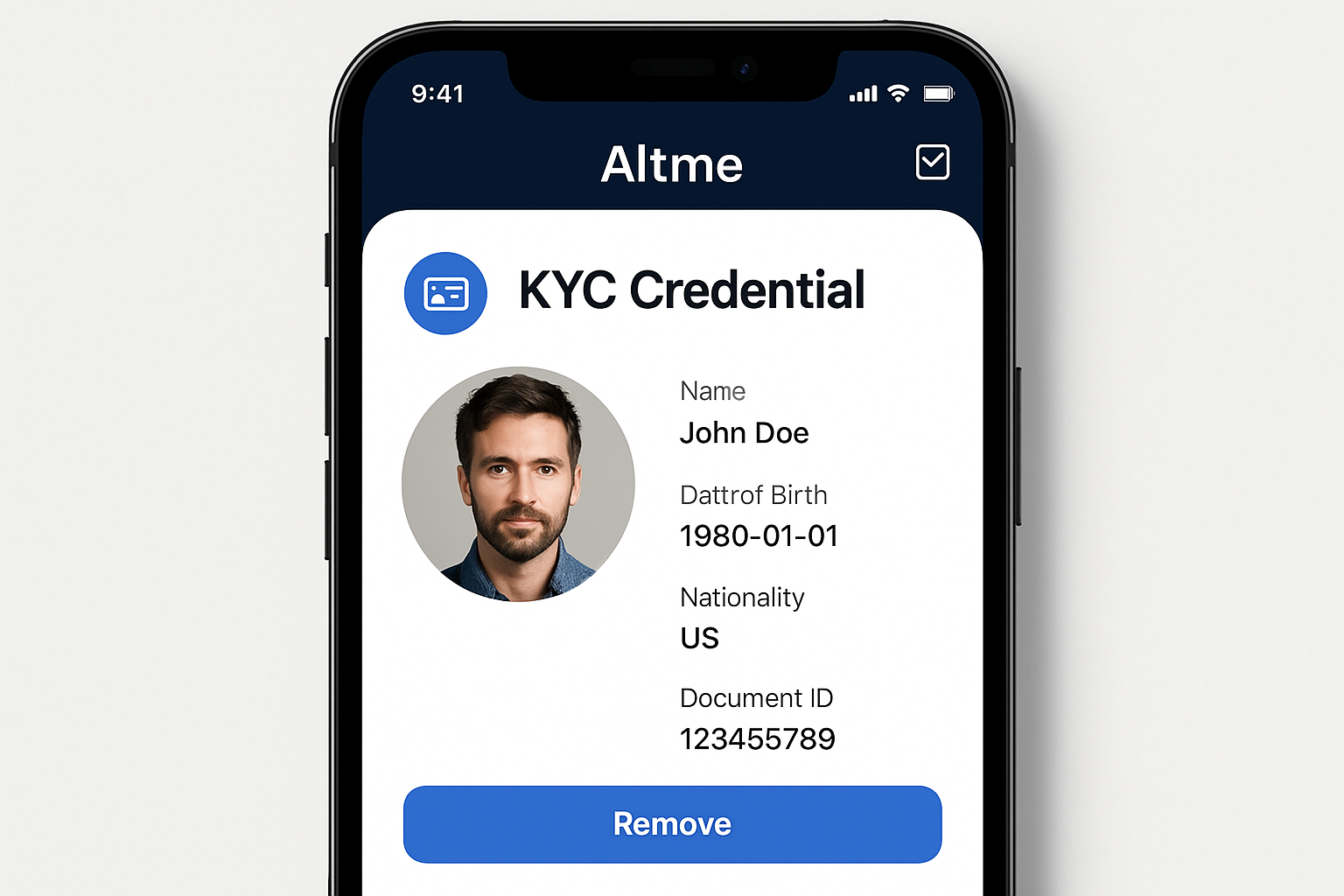
Privacy-Preserving Credentials: Solutions such as Altme issue verifiable credentials and non-transferable NFTs, letting users prove compliance without exposing personal data, aligning with privacy regulations like GDPR.
-
Cross-Chain Interoperability: Protocols including Altme and Sign Protocol support blockchain-agnostic attestations, allowing users to carry verified credentials across multiple dApps and chains.
-
Automated Compliance Enforcement: Chainlink Automated Compliance Engine (ACE) lets developers embed real-time compliance checks directly into smart contracts, ensuring only authorized users can access sensitive functions or assets.
These efficiencies translate directly to lower costs, both in terms of gas fees (due to optimized contract interactions) and reduced engineering hours spent reinventing compliance workflows.
Looking Ahead: Interoperability as a Growth Engine
The true power of decentralized identity attestations lies in their interoperability. As standards like EIP-712 and Verifiable Credentials gain traction, users will be able to carry their KYCed address verification across any compatible dApp or chain. This composability unlocks new models for cross-platform allowlists, collaborative token sales, and privacy-preserving community access.
This paradigm shift also positions projects to adapt rapidly as regulatory frameworks evolve globally. With compliance logic embedded at the protocol level, and verifications visible on-chain, audits become more transparent and less resource-intensive.
“Decentralized identity isn’t just a buzzword, it’s the foundation for scalable, compliant growth in Web3. “
If you’re considering whether to implement blockchain KYC solutions, the data points toward an inevitable industry standardization around onchain attestations. The benefits are measurable: faster onboarding, reduced risk exposure, improved privacy alignment, and seamless cross-platform user journeys.
The next phase of Web3 innovation will be built by projects that embrace these tools early, delivering superior compliance outcomes without sacrificing user autonomy or privacy. To explore technical best practices or start building your own secure allowlist system using attested KYCed addresses, visit our guide at /building-a-secure-allowlist-with-onchain-attested-kyced-addresses.






